Food Technology That Accelerates Food Production

Food technology refers to a mixture of “food” as well as “technology.” If we think of the industries that are connected to food, many people imagine things such as food processing and manufacturing, as well as food establishments. For a long time, these sectors have often been viewed as largely unrelated to modern technology. In reality, they are now excellent areas of application for technological advancements, including ICT robotics, robotics, and biotechnology. Each day, businesses are constantly introducing new technologies to boost the efficiency of production as well as to create functional food items that streamline consumption and distribution, respond to the changing requirements of the consumer, and even eliminate labour shortages. One of the main factors that have brought food technology up to speed is the development of technologies to classify ingredients and food technology as industrial items built on technology and science. The food we purchase in the grocery store is mostly made by industrial processes. Agricultural raw materials, like grains, are processed through a variety of stages before being offered as food. Through the process, it is changed in terms of physical, chemical, and microbiological. This is why food technology is a multidisciplinary engineering science. The bachelor’s program in food technology gives students instruction in the field of food engineering on a scholarly basis. The whole process of food production (“From Farm to Fork”) is examined from a technical, technological, scientific, and economic standpoint. A large portion of food processed in the food sector is life. Naturally, every product is unique and has an environment that alters as time passes.
Because of this, unlike electronic devices or automobiles that can be mass-produced and standardized stably, it was a challenge for producers to deal with these products, since their growth and production were not precisely monitored. As an example, robotics were not able to complete tasks that humans would be able to do, for example, grasping and placing uneven, soft strawberries. Innovations in Information Processing Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) that uncovers relevant trends in diverse types of individuals, technology like the Internet of Things (IoT) that allows us to analyse and understand personal differences, as well as biotechnology, which enables us to regulate and monitor the characteristics of animals, as well as plants, have allowed us to adopt a new method of industrialising food technology. Furthermore, the massive size and continued growth of the food and beverage industry can be a reason for the increasing focus on food technology. As per the Policy Research Institute, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries The global market for food and beverages is projected to expand 1.5 times over time, going from 890 trillion yen in the year 2015 up to 1,360 trillion yen by the year 2030. Since the market for applications is enormous and likely to continue growing, it is a great opportunity to put a lot of money into developing technology that can solve the problems that exist in the market, and create value. A few countries have implemented guidelines that promote food technology as an industry that is growing. In Japan, the Council for Public-Private Partnership in Food Technology was created in 2020 by the Japanese government, in conjunction with academics, industry, and the government to encourage innovative solutions for food technology and other initiatives.
Utilizing Food Technology to Try and Eliminate Food Crises and Losses

What kind of technology is used to address the social problems related to food and create value? Here is a list of projects in two common regions. In the first, there are measures for tackling hunger crises. By 2050, the planet’s global population is predicted to increase by around 30% from what it is currently. There is no doubt that food technology demand is expected to increase with this. There are also fears that climate change as a result of global warming could make it difficult to grow crops in locations that are suitable for growing. As part of the SDGs, the second one is to achieve “zero hunger.” To address the problems Biotechnology is used in the development of cultured meats through layers of animal cells before creating them using 3D printers to design cultivars that thrive in difficult conditions, with high yields.
Innovative techniques for fisheries and agriculture, including plant factories as well as onshore fisheries with artificial growth environments, are currently being put into application. Through the expansion of these techniques and methods, we’re not just growing yields but unlocking the power inherent in the genes of plants and animals to create foods with several ingredients that can be effective in improving the health of humans. Second, we can eliminate the problem of food waste.
Food Technology and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations

Approximately one-third of foods that are part of food technology, from the production of agricultural products to consumption, are wasted due to a myriad of reasons. This amounts to around 1.3 billion metric tonnes annually. In Japan in particular, where the quality of food is a major concern and a common commercial practice that encourages losses because of the “one-third rule.” According to this principle, the delivery- and sell-by dates are defined by dividing the duration beginning with the production date and ending at the date of expiration by three, which means that the item is removed after every period. The Japanese government is working on a solution to the procedure. The SDGs are also a set of goals to reduce food waste by half per person at the consumer and retail levels, as well as decrease food loss within the supply chain, the production process, and post-harvest losses in 2030. Modern food chain management that makes use of RFID tags, as well as the Internet of Things, is crucial to reducing the problem of food loss. It is the goal to be aware of the chain’s distribution patterns for food products and enable it to react to changes in the product’s condition by making it the raw material used in processing food items when the date for the best-by of food technology is approaching. If these techniques are used, it will also be possible to create traceability, which will ensure the safety of food by preventing fraud about the place of origin as well as tracking foreign chemicals, which include allergens, additives, and halal compliance.
Food Service Sustainable Dining
]]>Higher Education’s Customer Satisfaction

Through a review of the studies on customer satisfaction, it is evident that there exists a vast amount of research that examines customer satisfaction within both the public and private business sectors. Within the realm of higher education, only a few research studies on the satisfaction of customers were conducted. Based on Navarro and Iglesias. Several efforts have been undertaken by scholars to establish satisfaction as a concept about the services provided within higher education. They believe satisfaction is the ultimate condition of psychological processing. Amelia and Garg reported that the initial impression is the most important factor, along with the high quality and properness of the food, as well as the kindness of the personnel in their service. At university cafeterias, college students represent the largest portion of customers’ satisfaction with the institution’s food service, therefore, the food services on campus are increasing in importance and popularity. It took into consideration gender differences in his research on the effects of the food service attributes at campuses on satisfaction, perceived value, and attitudes of consumers. In the study of Garg and Kumar Garg and Kumar. The eating experience can affect the loyalty and satisfaction of staff as well as students and patrons. In the cafeterias at universities, where customers are served, satisfaction is directly related to the high-quality food and beverage selection and variety, as well as cleanliness and hygiene, as well as the fairness of price and value. In light of the above characteristics, there are a variety of variables that influence consumers in their decision-making process when it comes to food. Studies have indicated that the level of satisfaction in the cafeterias at universities depends on the quality of food and beverages.
Quality of Food Service

The quality of food service refers to the features of food that are suitable for the consumer. The quality of the overall drinks and foods, such as the flavor, nutritional aspect, freshness, and even the amount, is categorized as a measurement of quality in food. Being a fundamental product in the food service industry, the quality of food and beverages has been assigned high importance, and they have been inspected on a variety of aspects, including temperatures, texture, flavour, and scent. The quality of the food and drinks can affect consumers’ desire to return to a particular establishment. It was found that there was a significant positive relationship between the satisfaction of consumers with the food and drink quality and the likelihood of them eating at the same establishment. In addition, the eating habits of workers are often associated with low-quality food and bad choices on the menu that can have negative effects. They have outlined a variety of ways to encourage customers to make healthier choices. Institutions must offer a setting that makes it easy for students to make healthy food choices. Recent research has revealed that a lot of establishments have food services that are stuffed with high-calorie, nutrient-poor foods that are heavily marketed in the form of advertisements. Furthermore, it’s the job of operators to offer a wide range of items on their menus to give their customers greater choices to select from. Menus are a crucial window into the restaurant’s marketing tactics. Not always is the menu the most important factor. The important objective of the look is to assess the critiques of cafeteria shoppers about their delight with specialty foods and drinks in addition to the offerings presented at the university cafeteria. By giving respondents greater time to finish the questionnaire, which should make it less complicated for them to reply, a quantitative research approach is used to check the hypotheses of the study. This technique is based on the distribution of partially completed questionnaires. This involves collecting information from customers, which can be examined statistically. The intended population for the study was the entire academic staff, academics, and students of the university, which is located in rural Lebanon. According to official data from the university’s 2018–19 academic year, there are more than 6,600 enrolled college members, groups of workers, participants, and college students. Given this huge amount, it’s difficult to employ random sampling methods. So, a convenience method of sampling is the ideal way to collect data for this study. About the newly formed administration body at the university, the university is now working by employing various strategies to boost the retention of students. The strategies include choosing and prioritizing key motivations for students’ recruitment, and appropriate retention strategies. The management committee of the university decided to include students in the process of making decisions regarding food service, and also in other areas of service and academics. Management requested that there be a system in which the cafeteria’s operator is continuously monitored by students as well as other patrons, which will also have an impact on the evaluation of catering services offered on campus. The newly formed management committee of the university will be monitoring improvements over the next five years to evaluate the effectiveness of their services based on students’ feedback, and also to determine points that need further focus. The current questionnaire study is based on an earlier validated instrument employed by El-Said and Fathy, with some modifications.
Research Method and Sampling Technique

Comparatively to El-Said and Fathy, this questionnaire has greater types (academics and employees) to give more accurate findings and increase universality. The sample was divided into two parts. The first is targeted to collect demographic information about cafeteria patrons and their behaviour particulars (academic staff, students’ gender, gender, and age, as well as the number of times they visit the cafeteria, monthly spending, and the desire to keep dining at the caféteria). The second part of the survey consisted of four sections. The statements in these sections were taken from the DINESERV questionnaire. DINESERV is an adaptation of the SERVQUAL instrument that was invented by Barsky and adapted to be used in the industry of food service. The initial part of the second segment comprised eight questions, which were aimed at assessing customer perceptions about the high-quality food and drinks served in the cafeteria. The second section comprised five statements that were aimed at assessing customer perceptions regarding the quality of service within the cafeteria. The third section comprised five sentences that were intended to gauge their perceptions of the overall quality of the environment. The fourth portion of Section 2 was designed to gauge how customers’ views of the cost versus what they get. The last section is designed to gauge customer satisfaction overall regarding their general satisfaction with food and beverages, their overall satisfaction with the service, their overall satisfaction with the high-quality of the restaurant, and their overall satisfaction with the amount they paid for the service compared to what they got for it, as well as their overall satisfaction with dining service. The point scale of Likert can be utilized for evaluating satisfaction, with being the highest level. content, extremely satisfied, and satisfied, neutral. In addition, the university’s food service provider must pay greater attention to the standard of the environment. The cafeteria should be designed with care areas and interiors that provide an inviting and relaxing atmosphere that will attract new patrons and keep existing ones. Food service providers at universities must maintain sanitation and cleanliness of the facilities to a high standard. These findings align with earlier results from Kim and colleagues. Enhancing customer satisfaction in a high-quality environment is not just a way to increase client loyalty but also enhances the reputation of the establishment and can be beneficial for business. Lugosi has analyzed the experience of food on campus for the well-being of students and has focused on the dining halls on campus as a space for coworking. In addition to the many factors that drive social interactions, modern designs of campuses at universities have taken on several of the characteristics of coworking spaces, including furniture and the layout of the structure that facilitate an enjoyable experience. In particular, hygiene or cleanliness was the second most crucial aspect, following food selection and the convenience of location, that affected the choice of restaurant to eat at. Even though consumers are more aware of the nutritional quality of the food items they eat, food safety is still much more crucial than the risks associated with them. Hygiene in food service is crucial. Fatimah and her colleagues, through their research, have identified four key elements of food hygiene from the perspective of consumers that include food and place of service personnel and handling, as well as the premise, practices, and premises, and the scent of the environment. Priority should be given to quality service. Poor service quality can be attributed to poor quality food and beverage services. Additionally, consumers tend to be least satisfied with the value they are paying for the quality of the food and beverage items served. The food service provider at the university must enhance the quality of items served, and provide reasonable prices to stop customers from using other on-campus eateries, which would cause revenue loss and lower sales in the long term. The higher satisfaction of customers will boost the likelihood of returning to them and also provide positive word-of-mouth praise for the food service establishment.
Food Places Spice Up Your Life
]]>What is Food Panda?

Food Panda can be described as an online food delivery and ordering platform that connects consumers with restaurants in their area. With user-friendly platforms that make searching menus on various websites simple, ordering delicious dishes for affordable prices becomes possible, and delicious cuisine can be purchased with just the click of a smartphone screen! Foodpanda company models can leave companies feeling confused. There can be various concerns surrounding its operations, such as, for example, what its ways are of generating revenue or any potential benefits it could bring them. Questions remain. Visit this post for a thorough understanding of food delivery and ordering platforms. Most companies utilize apps on demand that enable them to meet customers’ growing expectations more easily. Food apps have long been part of the on-demand economy. Their simple psychological appeal attracts users while providing time and effort savings. The food delivery revenue sector is expected to see considerable expansion, with an eventual market valuation of approximately US$1.02 trillion by 2024. Food Panda and similar apps will play an increasingly vital role in helping us save both effort and time in 2024, offering customers convenience across their touchpoints with their on-demand service. We will gain insight into this vast food industry company to gain a clear view of its revenue model and business strategies.
Success Story Of Food Panda In the Food Business
Food Panda is an international online food delivery platform present in over fifty countries worldwide, including Bulgaria, Asia Pacific, and Romania. Managed by German company Delivery Hero SE with offices based out of Berlin, Foodpanda offers food delivery anywhere in its service areas. Foodpanda provides foodies with an effortless platform for ordering their favourite meals from local eateries across 246 cities worldwide, offering over 15,000 restaurants as partners on its platform. Foodpanda partners with over an estimated 80,000 riders for delivery. Deliver Hero acquired its business in December 2016. In India, Ola acquired Foodpanda operations for between $40 and $50 million on December 29th, 2017. Food Panda sold their Delivery Club division for $100 million to mail.ru in Russia in 2016, while Rocket Internet, their biggest shareholder, sold Foodpanda to German rival Delivery Hero and adopted their logo of pink instead of orange in 2017, respectively. Tech major Delivery Hero promptly followed Foodpanda into rebranding itself, offering exclusive discounts and promotions designed to increase customers using its platform. By 2018, Foodpanda had processed around three lakh orders each day, while this figure rose to over five lakh by 2019 alone. Ola is suspending Foodpanda food delivery service this year and has laid off more than 1500 “food delivery executives.” Food Panda operates under its in-house brands known as cloud kitchens, an idea adopted by Ola when purchasing Holachef in 2018. In 2019, their business will only include three private labels within this sector, such as The Great Khichd Experiment and FLRT. Foodpanda has raised $318 million in venture capital funding over its history. Foodpanda successfully raised an initial round of financing through Rocket Internet, AB Kinnevik, Phenomen Ventures, and MENA Holdings in 2013. That year also marked when Phenomen Ventures made an $8 million investment in Foodpand. That same year, its investors and Phenomen Ventures each invested $20 million, respectively, in an initial round. By 2014, Foodpanda announced they had amassed $60 million across various investor pools by 2015, while Goldman Sachs announced investing $100 million in Foodpanda during a short period! Foodpanda’s founders were Luke Nagel and Rico Wyder, who established it in 2012 in Berlin, Germany, with headquarters nearby. Foodpanda now stands at $6 billion+, while funding comes from Rocket Internet as well as other investors totaling $100 million in capital funding. Statista reports indicate that Food Panda received approximately 8.7 million orders during its inaugural year alone in 2014. By 2015’s end, however, they had managed to process over 22 million.
How Does Food Panda Work?

Food Panda is an exciting platform that facilitates restaurants offering excellent services directly to patrons who would prefer delivery of their meals directly to their homes. Foodpanda makes money through delivery costs while simultaneously cutting its operating costs through different strategies, which include:
- Special discounts may apply when making bulk purchases
- Creating stronger networks to ensure timely food deliveries
- Collecting cash before delivery and advertising fees
- Deliver different kinds of items beyond food delivery
Foodpanda has received much media coverage due to its focus on each of the phrases listed above, especially as on-demand apps have come into focus over recent years. More businesses have decided to invest in service on demand, with plans such as creating their own advanced Food Panda replica application to offer customers effortless food deliveries at all hours. Check out this video of Foodpanda’s process of providing timely deliveries of meals directly to customers’ doors! Food lovers can browse the menus of nearby restaurants as well as their specialty dishes and meals. Customers place orders with them, who in turn give orders directly to restaurants, who then prepare and cook food and prepare delivery service providers accordingly for delivery service providers to deliver it directly. Eventually, it takes over by giving orders directly to delivery service providers, who then distribute orders directly. Our delivery service delivers food directly to our clients’ addresses, while phase 5 paying customers make payments and provide feedback based on their experience with it. Foodbanda provides simple and dependable operation of Foodpanda-esque applications like Foodpanda for those passionate about food or restaurants alike. If your business requires long-term development strategies to thrive, then consider investing in similar apps as a possible way forward. Foodpanda Business Model Canvas For food lovers everywhere, Foodpanda provides an exquisite and flavorful dining experience like no other. Their platform has effectively eliminated the necessity to travel to restaurants since foodies can get it delivered directly to their homes via ordering food online. Food Panda links them directly with nearby restaurant options they prefer and connects customers directly. Learn everything there is to know about what the system does as well as their business model today. Don’t wait; learn it right now. Foodpanda provides customers with delicious, nutritious, and exceptional dining experiences; there is no need to go anywhere for meals anymore, all thanks to an online ordering system connecting eateries directly with nearby restaurants of their preferred choice. Discover everything this system does and its business model within just minutes.
Consumer Groups

Food Panda provides significant value proposition advantages to its platform users: access, convenience, personalisation of branding status as a brand status savings and cost reductions. Foodpanda makes advertising products to those unable to visit an actual physical location simpler while making shopping online simpler for food shops themselves. Customers can place orders using an easy and intuitive system; they can make orders any time of the day via the site without hassle or issues; additionally, they have the choice of picking up or having items delivered right to them; and they can pay using any method suitable to them. The system allows customers to customize the experience by categorizing restaurants according to type. Furthermore, its offers, such as food discounts and free delivery, encourage customer interaction as they try new products while saving costs. Foodpanda has earned itself an exceptional reputation thanks to its rapid business expansion, currently covering around 500 cities in 24 different countries and receiving accolades such as winning the European Tech Startup Award 2014 in “Best E-commerce Startup.” Foodpanda operates with a cost-driven model to maximize sales at its stores while simultaneously decreasing expenditures and expenses, both manually and via automated systems. Primary drivers for expenditure on this website include marketing and sales expenses as well as fixed expenditures such as customer support and administration charges or administrative overhead fees. Foodpanda derives its primary income stream from restaurant commissions it has established through partnerships. According to one report, over 40% of Foodpanda’s revenue comes through delivery, and 10% comes through advertising. There are multiple other avenues through which Foodpanda generates funds; explore for yourself. Digitalization has led to an explosion of food delivery right to our homes, turning dining out into more of an at-home dining experience than ever. Modern-day foodies prefer customised meal delivery services at home, such as Food Panda, that remove the hassles associated with managing and finding delivery companies. Foodpanda turns around $100 into $150 when signing up, and Foodpanda offers businesses an advertising service through which they can market their business through an interactive site such as its platform. Businesses pay monthly advertising fees on Food Panda to take part. Foodpanda charges an applicable delivery charge on each ordered shipment that depends upon its area. Users visiting Foodpanda’s app or website will see payment options like credit or debit cards as well as methods of making payments available via any number of platforms, such as credit, debit, F&I cards, etc., making payments more flexible. Foodpanda charges an affiliate revenue source fee from both banks offering these payment services directly, which provides another avenue of income generation for Foodpanda. Foodpanda promises around 20% commission for orders users place through its platform, saving restaurants time and money by not covering electric bills, rent costs, and other related service-related costs for service delivery, yielding substantial profits for Foodpanda service providers. Food Panda may have experienced various obstacles along its journey as an online delivery platform, yet they have managed to overcome all challenges to remain viable. Their rapid expansion can be traced to customers preferring online services over physical ones; similarly, their platform gives users seamless customer service by offering direct deliveries directly to users’ homes; they also have a large market presence as a large audience subscribes; and additionally, you could create sophisticated delivery platforms within organisations too.
Food Chain from Farm to Fork
]]>What is a food chain?
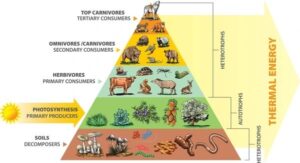
A food chain refers to an ecological process in which living things consume each other before being devoured by larger organisms. Energy and nutrients flow across species at various trophic levels in an ecosystem in a manner known as a “feedback loop.”. Trophic levels refer to various stages in this chain, beginning from producers at its base up to primary, secondary, and third consumers; each stage is known as a trophic stage in this food chain. A food chain comprises several main parts. Producers are autotrophs like phytoplankton, cyanobacteria, algae, and green plants that generate food through photosynthesis using solar energy for fuel. These producers form their foundation by using sunlight’s power to make food from nothing! Producers may include any organism, plant, or animal that utilizes photosynthesis for its sustenance needs, with organisms being autotrophs due to producing what they consume via photosynthesis being considered producers in general terms. Consumers refer to organisms that rely on other living organisms or plants for sustenance. A food web comprises almost all living creatures, as consumers rely heavily on each other as food sources. Consumers include herbivores that consume plants, carnivores who feed on other species for sustenance, parasites who inhabit certain organisms to harm them, and parasites who reside on certain individuals to harm them, as well as scavengers who consume decomposing carcasses after creatures have passed on, plus scavengers who consume deceased animal carcasses from consumption by other consumers—an integral component of any food web! Herbivores in this case can be considered primary consumers, while carnivores represent second-tier consumers. Both species inhabiting the second trophic layer consume producers. Therefore, herbivores, or primary consumers, include people residing within that second layer. Decomposers, organisms that derive strength from waste or lifeless natural material, represent the very last degree inside the meal chain. Decomposers play a necessary role in offering critical nutrients to soil by breaking down organic fabric into inorganic materials, which provide critical nourishment to soil ecosystems. Decomposers play an essential part in recycling substances they ingest by returning minerals into oceans or soil, where producers or autotrophs may utilize them in turn, starting a fresh food chain that extends across multiple food chains within an interlinked food web. Food webs resemble chains of food in that both consist of interlinked species eating each other; in some instances, an individual species might even be consumed by multiple predators or by multiple other species; this explains why so much of tropical biodiversity lies within one system. Food chains don’t accurately demonstrate energy flow. In contrast, the food web provides the right visualization as it shows interactions among species. With more interrelationships between various food chains forming their structure and becoming increasingly complicated over time,. Such complexity could ultimately contribute to an ecologically sustainable system.
Food Chain Integrity

Integrity is multifaceted when considering food supply chains from producer to consumer, from producers through all stages. Modern food chain integrity measures centre around factors including the microbiological and chemical safety of foodstuffs as well as source integrity (authenticity of source), fraud detection, and quality assessments. Sooner or later, customers will expect products to meet more stringent eco-friendly, animal welfare-oriented, no-child labor-free criteria, as well as trade with emerging nations’ standards for the production of high-integrity food. Food businesses must transform such consumer sentiments into objective standards for producing food with integrity. Detritus Food ChainThe detritus food chain includes various living organisms as well as plant species like algae, bacteria, and fungi, as well as protozoa and insect mites, among others. Decomposers begin feeding off dead organic matter; energy from food then gets converted to decomposers, which in turn become food sources for detritivores and decomposers, which later feed carnivorous organisms such as maggots, which become food for larger carnivorous organisms such as snakes, frogs, etc. Primary consumers include protozoans Fungi bacteria, among others, feed off decayed organic debris, while other consumers include protozoans Fungi feed off decayed material that feeds off debris before moving back upstream again into food chains that begin. One type of food chain known as food chain grazing begins with green plants and then moves on through herbivores before becoming carnivorous. With such an ecosystem in place, energy for photosynthesis becomes limited at the foundational levels of food chains, grazing or otherwise. At the root of it all lies the energy exchange between herbivores and autotrophs; from here, energy can travel back down through this food chain until reaching herbivores again for consumption. As autotrophs form the basis of nearly all ecosystems on Earth, most food chains worldwide follow this particular model of sustenance distribution. Such chains facilitate both local and international commerce through complex flows. Supply and exchange chains may both play an integral part. Regulations enforced by intergovernmental bodies provide structure for this market, while social input raises standards through private industry participation. As part of global trade in food chains, small farmers cannot participate in large portions of production both globally and locally. To illustrate its complexity in India, the United States is shown as a component in this chain. Humans play various roles within a food chain depending on what they consume as sustenance. If humans only eat plants as sustenance, then their role as primary consumers would be clear; otherwise, they are called secondary or omnivore consumers, respectively. Animals too are consumers in food chains since they consume both plants and other animals that consume plants in one way or another as consumers, producers make food, consumers eat it up before it finally ends with predators taking it all down through one continuous pathway into energy flow pathways of various sorts (in food chains it all starts from producers making food production to being eaten upstream of producers by producers making food production all the way up until topmost predators at last) where energy flows down one path while food webs present multiple energy flow paths between organisms eating multiple items consuming an organism consumes multiple items, unlike food chains where energy flows one way only through one path for energy flow while one way flow exists between producers producing energy flow pathways from one stage of energy flow while there can be multiple paths through which energy flows between various organisms in that particular chain or web structure where energy flow follows one path), one path than another when considering energy flow within this complex system of course.
Farm-to-Market Food Chain
A food chain refers to the complex distribution system for both locally produced food items as well as international supplies of them and serves both as supply and value chains. Many regulations imposed by international organizations act as the foundation for these markets. Social contributions also raise standards by engaging the private sector. Unfortunately, global trade within food supply chains kept small-scale farmers out of much of global production as well as local markets. To demonstrate the complexity of food chains in both India and America, different components from both chains have been displayed here. Strong top-down influence can result in cascading cascades of trophic elements within these food chains. One of the best-studied food chains can be found in mid-latitude lakes, where researchers have conducted extensive food chain analyses. Zooplankton and phytoplankton serve as key links between plants and herbivores, providing crucial food. These large zooplankton lakes remove phytoplankton from water at an extremely rapid pace, making them one of the world’s biggest herbivores. Lakes that contain only low concentrations of planktivorous fish tend to experience lower phytoplankton densities due to the large species of zooplankton that thrive at such conditions, significantly diminishing phytoplankton populations during the midsummer months and becoming clear. Planktivorous fish provide enough planktivorous to reduce zooplankton numbers in lakes that contain enough planktivores that consume it, mitigating any negative impacts from phytoplankton-zooplankton interactions in the summer months. Consequentially, water becomes opaque with phytoplankton blooms during that season, creating an “upward cascade of planktivores to phytoplankton.” Lakes with large piscivorous species like wall-eyed pike extend four links in their chain, and planktivorous fish populations decrease, freeing Zooplankton populations from predation. Knowledge of food chains is vitally important because it reveals intricate relationships within an ecosystem, how organisms rely on each other for survival, and how energy moves within this system. Understanding food chains helps reveal these complex interrelations as they illustrate energy flow within it and thus show us where resources lie in an ecosphere.